.png) The Cartesian operator inputs two arrays and outputs a single array. The two arrays must be structured as a table with two rows because this operator only has one input port. This new array contains each possible combination of the source arrays’ values. The output displays as a set of ordered pairs. For example, source arrays of
The Cartesian operator inputs two arrays and outputs a single array. The two arrays must be structured as a table with two rows because this operator only has one input port. This new array contains each possible combination of the source arrays’ values. The output displays as a set of ordered pairs. For example, source arrays of ["A", "B"] and [1,2] produce the combinations [["A",1], ["A",2], ["B",1], ["B",2]]. This function is like a Cross Join, or Cartesian Product, in SQL coding language.
A common comparison involves a deck of cards. A standard deck includes an array of 13 different values (two, three, four, and so on), when considering the cards by rank. But, when considering the cards by suits, the deck includes an array of four values (clubs, hearts, spades, and diamonds). If you apply the Cartesian operator to these two arrays, the output is a single array of 52 ordered pairs. Each ordered pair represents a card in the deck.
This operator lets you create all possible combinations using rows of data. Let’s say you’re tracking the success of your company's marketing strategies. The Cartesian operator helps track the success of these strategies across different demographics. You can use the Cartesian operator to generate the combinations of that data.
You’ll find the Cartesian operator in the Table group to the left of the Data Workflow canvas.
About the Info Window
Here's a breakdown of each setting in the Info window:
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Category | Grayed out and non-adjustable setting indicating the operation type. |
Label | Sets the label for your operator, displaying below the operator on your Data Workflow canvas. This field is optional, but set a label if you use more than one of the same operator type. A label helps you identify your operators without opening any Info windows. |
Preserve Argument Type | When selected, this setting ensures the argument data type is respected when the operator executes. |
Type | Select an option from the drop-down to determine how to input the data. You can select an array or a comma-separated list. |
Field Label | Enter the field/key you want the Cartesian operator to act on. This is the name of the two arrays. |
Adding a Cartesian Operator
To see this operator in action, you'll create a simple module. You'll begin with some sample data and use a Data Workflow and Cartesian operator to view all of the possible combinations.
These instructions assume that you have a new module open, saved, and with a title.
Configure the Data Table Component
Begin with a two-column Data Table component. Column A stores the values x, y, z, and Column B stores the values 1, 2, 3. There are nine ordered pairs after you pass the data to a Cartesian operator.
In the Module Builder, drag and drop a Data Table component onto your canvas.
In the Property ID field, enter
dtSampleData.In the data table, enter the following:
#
A
B
1
x
1
2
y
2
3
z
3
.png)
Click Save Component.
Configure your Data Workflow Component
Use an Input operator to bring your data into the Data Workflow. From there, use two Col2Array operators to convert your data table into two separate arrays. Then, pass the data to a Create Table operator and two Set operators to pass the arrays as one input to your Cartesian operator. Lastly, connect your Cartesian operator to a Console operator to view the results.
Drag and drop a Data Workflow component onto your canvas, placing it below your Data Table component.
In the Property ID and Canvas Label Text fields, enter
dwfCartesian.
Configure the Input Operator
Use an Input operator to bring your data into the Data Workflow.
Drag and drop an Input operator onto your Data Workflow canvas.
Configure the operator’s Info window as follows:
Setting
Value
Category
Input
Component
dtSampleData
Required
Yes
Source
Default
Configure the First Col2Array Operator
This operator converts Column A from your data table to an array.
Drag and drop a Col2Array operator onto your Data Workflow canvas.
Configure the operator’s Info window as follows:
Setting
Value
Category
Col2Array
Label
Column A
Preserve Argument Type
.png) (unchecked)
(unchecked)Drop Empty
Path
A
Default Value
Connect the output port (right) of the
dtSampleDataInput operator to the input port (left) of theColumn ACol2Array operator.
Configure the Second Col2Array Operator
Set up the second Col2Array operator to convert Column B from your data table to an array.
Drag and drop another Col2Array operator onto your Data Workflow canvas.
Configure the operator’s Info window as follows:
Setting
Value
Category
Col2Array
Label
Column B
Preserve Argument Type
.png) (unchecked)
(unchecked)Drop Empty
Path
B
Default Value
Connect the output port (right) of the
dtSampleDataInput operator to the input port (left) of theColumn BCol2Array operator.
Configure the Create Table Operator
The Cartesian operator only allows one input, so you must bring your two arrays together. Use a Create Table operator and two Set operators to combine both arrays into a table.
Drag and drop a Create Table operator onto your Data Workflow canvas.
Configure the operator’s Info window as follows:
Setting | Value |
|---|---|
Category | Create Table |
Label | |
Preserve Argument Type |
|
Create Index | No |
Rows | 1 |
Configure the First Set Operator
Use two Set operators to add your arrays to your empty table. The first Set operator puts the values x, y, and z into the path [0].value. So, the array [x,y,z] is the output from the Column A Col2Array operator. The Set operator sets it as the value of an object at index 0 of the array.
Drag and drop a Set operator onto your Data Workflow canvas.
Configure the operator’s Info window as follows:
Setting
Value
Category
Set
Label
[0].value
Preserve Argument Type
.png) (unchecked)
(unchecked)Path
[0].value
Value
Connect the output port (right) of the Create Table operator to the upper input port (left) of the
[0].valueSet operator.Connect the output port (right) of the
Column ACol2Array operator to the bottom input port (left) of the[0].valueSet operator.
Configure the Second Set Operator
The second Set operator puts the values 1, 2, and 3 into the path [1].value of the same table. So, the array [1,2,3] is the output from the Column B Col2Array operator. The Set operator sets it as the value of an object at index 1 of the array.
Drag and drop another Set operator onto your Data Workflow canvas.
Configure the operator’s Info window as follows:
Setting
Value
Category
Set
Label
[1].value
Preserve Argument Type
.png) (unchecked)
(unchecked)Path
[1].value
Value
Connect the output port (right) of the
[0].valueSet operator to the upper input port (left) of the[1].valueSet operator.Connect the output port (right) of the
Column BCol2Array operator to the bottom input port (left) of the[1].valueSet operator.
Configure the Cartesian Operator
The Cartesian operator now arranges the values into an output of ordered pairs in a single array.
Drag and drop a Cartesian operator onto your Data Workflow canvas.
Configure the operator’s Info window as follows:
Setting
Value
Category
Cartesian
Label
Value
Preserve Argument Type
.png) (unchecked)
(unchecked)Type
Array
Field Label
value
Connect the output port (right) of the
[1].valueSet operator to the input port (left) of theValueCartesian operator.
Configure the Console Operator
A Console operator lets you view the outputs of your module in the DevTools Console. That way, you can ensure your Cartesian operator is configured correctly.
Drag and drop a Console operator onto your Data Workflow canvas.
Configure the operator’s Info window as follows:
Setting
Value
Category
Console
Label
Output
Connect the output port (right) of the
ValueCartesian operator to the input port (left) of theOutputConsole operator.Click Save Component.
.png)
Configure the Initializer Component
Lastly, add an Initializer component to trigger the Data Workflow.
Drag and drop an Initializer component onto your canvas, placing it above the Data Table component.
In the Property ID and Canvas Label Text fields, enter
initCartesian.From the Trigger Type drop-down, select New Submission.
In the Outputs table, enter the following:
#
Property ID
Type
Value
1
dwfCartesian
trigger
GO
.png)
Click Save Component.
Save your module.
The completed example looks like this in the Module Builder:
.png)
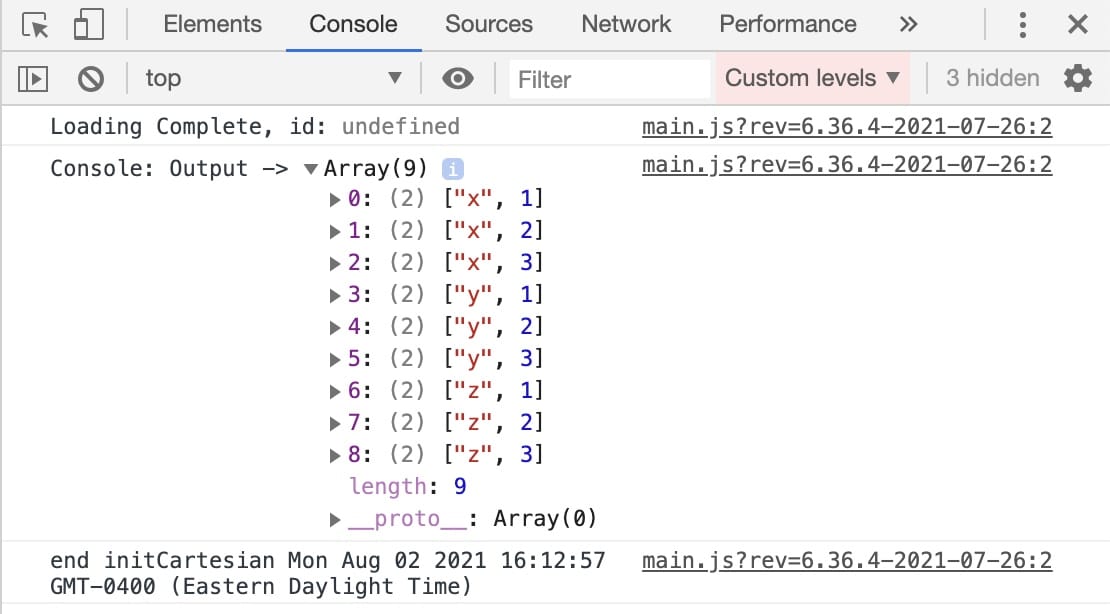
Now, test your Data Workflow by previewing your module in Express View and opening the DevTools Console. Your Output Console lists all the possible combinations of your data.
 The Cartesian operator inputs two arrays and outputs a single array. The two arrays must be structured as a table with two rows because this operator only has one input port. This new array contains each possible combination of the source arrays’ values. The output displays as a set of ordered pairs. For example, source arrays of
The Cartesian operator inputs two arrays and outputs a single array. The two arrays must be structured as a table with two rows because this operator only has one input port. This new array contains each possible combination of the source arrays’ values. The output displays as a set of ordered pairs. For example, source arrays of ["A", "B"] and [1,2] produce the combinations [["A",1], ["A",2], ["B",1], ["B",2]]. This function is like a Cross Join, or Cartesian Product, in SQL coding language.
A common comparison involves a deck of cards. A standard deck includes an array of 13 different values (two, three, four, and so on), when considering the cards by rank. But, when considering the cards by suits, the deck includes an array of four values (clubs, hearts, spades, and diamonds). If you apply the Cartesian operator to these two arrays, the output is a single array of 52 ordered pairs. Each ordered pair represents a card in the deck.
This operator lets you create all possible combinations using rows of data. Let’s say you’re tracking the success of your company's marketing strategies. The Cartesian operator helps track the success of these strategies across different demographics. You can use the Cartesian operator to generate the combinations of that data.
You’ll find the Cartesian operator in the Table group to the left of the Data Workflow canvas.
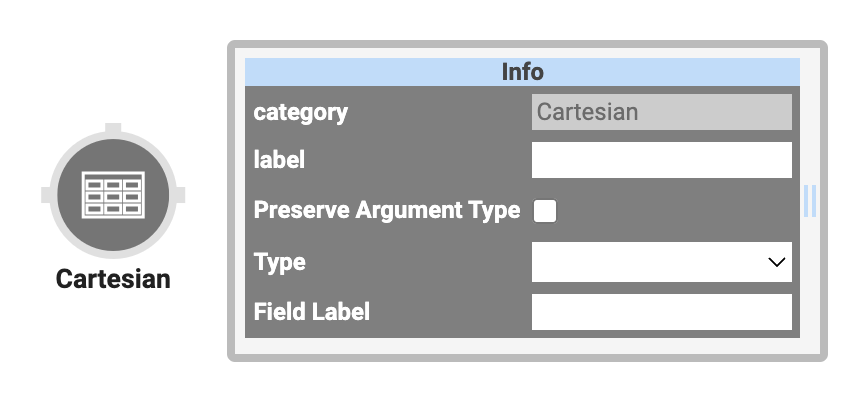
About the Info Window
Here's a breakdown of each setting in the Info window:
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Category | Grayed out and non-adjustable setting indicating the operation type. |
Label | Sets the label for your operator, displaying below the operator on your Data Workflow canvas. This field is optional, but set a label if you use more than one of the same operator type. A label helps you identify your operators without opening any Info windows. |
Preserve Argument Type | When selected, this setting ensures the argument data type is respected when the operator executes. |
Type | Select an option from the drop-down to determine how data is input. You can select an array or a comma-separated list. |
Field Label | Enter the field/key you want the Cartesian operator to act on. This is the name of the two arrays. |
Adding a Cartesian Operator
To see this operator in action, you'll create a simple module. You'll begin with some sample data and use a Data Workflow and Cartesian operator to view all of the possible combinations.
These instructions assume that you have a new module open, saved, and with a title.
Configure the Data Table Component
Begin with a two-column Data Table component. Column A stores the values x, y, z, and Column B stores the values 1, 2, 3. There are nine ordered pairs after you pass the data to a Cartesian operator.
In the Module Builder, drag and drop a Data Table component onto your canvas.
In the Property ID and Label fields, enter
dtSampleData.In the data table, enter the following:
A
B
1
x
1
2
y
2
3
z
3
.png)
Click Save.
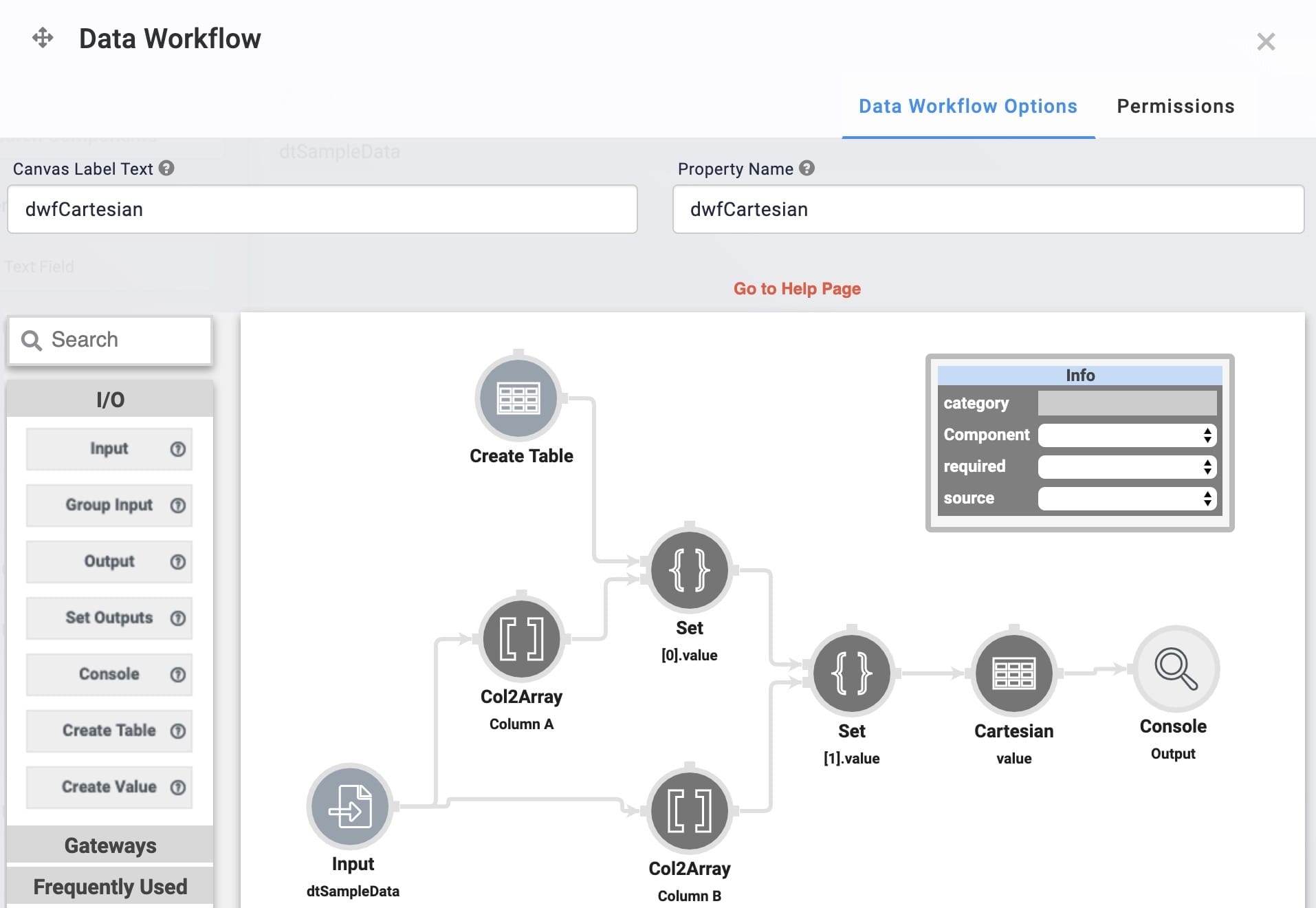
Configure your Data Workflow Component
Use an Input operator to bring your data into the Data Workflow. From there, use two Col2Array operators to convert your data table into two separate arrays. Then, pass the data to a Create Table operator and two Set operators to pass the arrays as one input to your Cartesian operator. Lastly, connect your Cartesian operator to a Console operator to view the results.
Drag and drop a Data Workflow component onto your canvas, placing it below your Data Table component.
In the Canvas Label Text and Property Name fields, enter
dwfCartesian.
Configure the Input Operator
Use an Input operator to bring your data into the Data Workflow.
Drag and drop an Input operator onto your Data Workflow canvas.
Configure the operator’s Info window as follows:
Setting
Value
Category
Input
Component
dtSampleData
Required
Yes
Source
Default
Configure the First Col2Array Operator
This operator converts Column A from your data table to an array.
Drag and drop a Col2Array operator onto your Data Workflow canvas.
Configure the operator’s Info window as follows:
Setting
Value
Category
Col2Array
Label
Column A
Preserve Argument Type
.png) (unchecked)
(unchecked)Drop Empty
Path
A
Default Value
Connect the output port (right) of the
dtSampleDataInput operator to the input port (left) of theColumn ACol2Array operator.
Configure the Second Col2Array Operator
Set up the second Col2Array operator. This operator turns Column B from your Data Table into an array.
Drag and drop another Col2Array operator onto your Data Workflow canvas.
Configure the operator’s Info window as follows:
Setting
Value
Category
Col2Array
Label
Column B
Preserve Argument Type
.png) (unchecked)
(unchecked)Drop Empty
Path
B
Default Value
Connect the output port (right) of the
dtSampleDataInput operator to the input port (left) of theColumn BCol2Array operator.
Configure the Create Table Operator
The Cartesian operator only allows one input, so you must bring your two arrays together. Use a Create Table operator and two Set operators to combine both arrays into a table.
Drag and drop a Create Table operator onto your Data Workflow canvas.
Configure the operator’s Info window as follows:
Setting
Value
Category
Create Table
Label
Preserve Argument Type
.png) (unchecked)
(unchecked)Create Index
No
Rows
1
Configure the First Set Operator
Use two Set operators to add your arrays to your empty table. The first Set operator puts the values x, y, and z into the path [0].value. So, the array [x,y,z] is the output from the Column A Col2Array operator. The Set operator sets it as the value of an object at index 0 of the array.
Drag and drop a Set operator onto your Data Workflow canvas.
Configure the operator’s Info window as follows:
Setting
Value
Category
Set
Label
[0].value
Preserve Argument Type
.png) (unchecked)
(unchecked)Path
[0].value
Value
Default Value
Connect the output port (right) of the Create Table operator to the upper input port (left) of the
[0].valueSet operator.Connect the output port (right) of the
Column ACol2Array operator to the bottom input port (left) of the[0].valueSet operator.
Configure the Second Set Operator
The second Set operator puts the values 1, 2, and 3 into the path [1].value of the same table. So, the array [1,2,3] is the output from the Column B Col2Array operator. The Set operator sets it as the value of an object at index 1 of the array.
Drag and drop another Set operator onto your Data Workflow canvas.
Configure the operator’s Info window as follows:
Setting
Value
Category
Set
Label
[1].value
Preserve Argument Type
.png) (unchecked)
(unchecked)Path
[1].value
Value
Default Value
Connect the output port (right) of the
[0].valueSet operator to the upper input port (left) of the[1].valueSet operator.Connect the output port (right) of the
Column BCol2Array operator to the bottom input port (left) of the[1].valueSet operator.
Configure the Cartesian Operator
The Cartesian operator now arranges the values into an output of ordered pairs in a single array.
Drag and drop a Cartesian operator onto your Data Workflow canvas.
Configure the operator’s Info window as follows:
Setting
Value
Category
Cartesian
Label
Value
Preserve Argument Type
.png) (unchecked)
(unchecked)Type
Array
Field Label
value
Connect the output port (right) of the
[1].valueSet operator to the input port (left) of theValueCartesian operator.
Configure the Console Operator
A Console operator lets you view the outputs of your module in the DevTools Console. That way, you can ensure your Cartesian operator is configured correctly.
Drag and drop a Console operator onto your Data Workflow canvas.
Configure the operator’s Info window as follows:
Setting
Value
Category
Console
Label
Output
Connect the output port (right) of the
ValueCartesian operator to the input port (left) of theOutputConsole operator.Click Save.
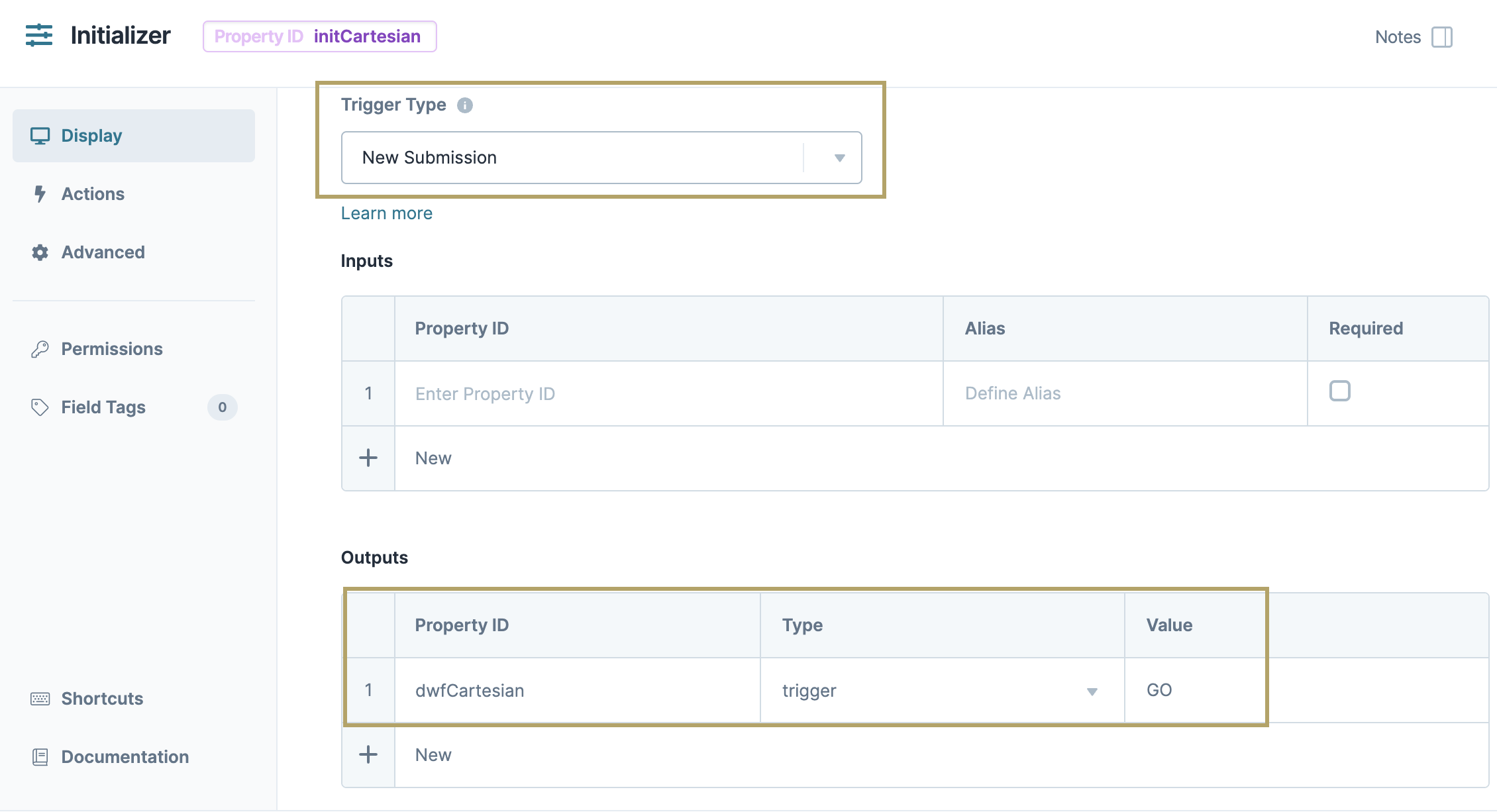
Configure the Initializer Component
Lastly, add an Initializer component to trigger the Data Workflow.
Drag and drop an Initializer component onto your canvas, placing it above the Data Table component.
In the Property ID and Canvas Label Text fields, enter
initCartesian.From the Trigger Type drop-down, select New Submission.
In the Outputs table, enter the following:
#
Property ID
Type
Value
1
dwfCartesian
Trigger
GO
Click Save & Close.
Save your module.
The completed example looks like this in the Module Builder:
.png)
Now, test your Data Workflow by previewing your module in Express View and opening the DevTools Console. Your Output Console lists all the possible combinations of your data.
