DWF (Data Workflow) Operators manipulate data inside the Data Workflow component. After placing a Data Workflow component on the Module Builder canvas, Creators can add DWF operators to retrieve, map, and manipulate data before sending it to another component. Much like components in a module, DWF operators connect together to perform complex operations.
Here are some common use cases for using the Data Workflow component and its operators:
Unwinding complex data structures.
Filtering data to obtain specific items.
Viewing data at different points in the Data Workflow.
Appending data to create new structures.
Applying formulas to data.
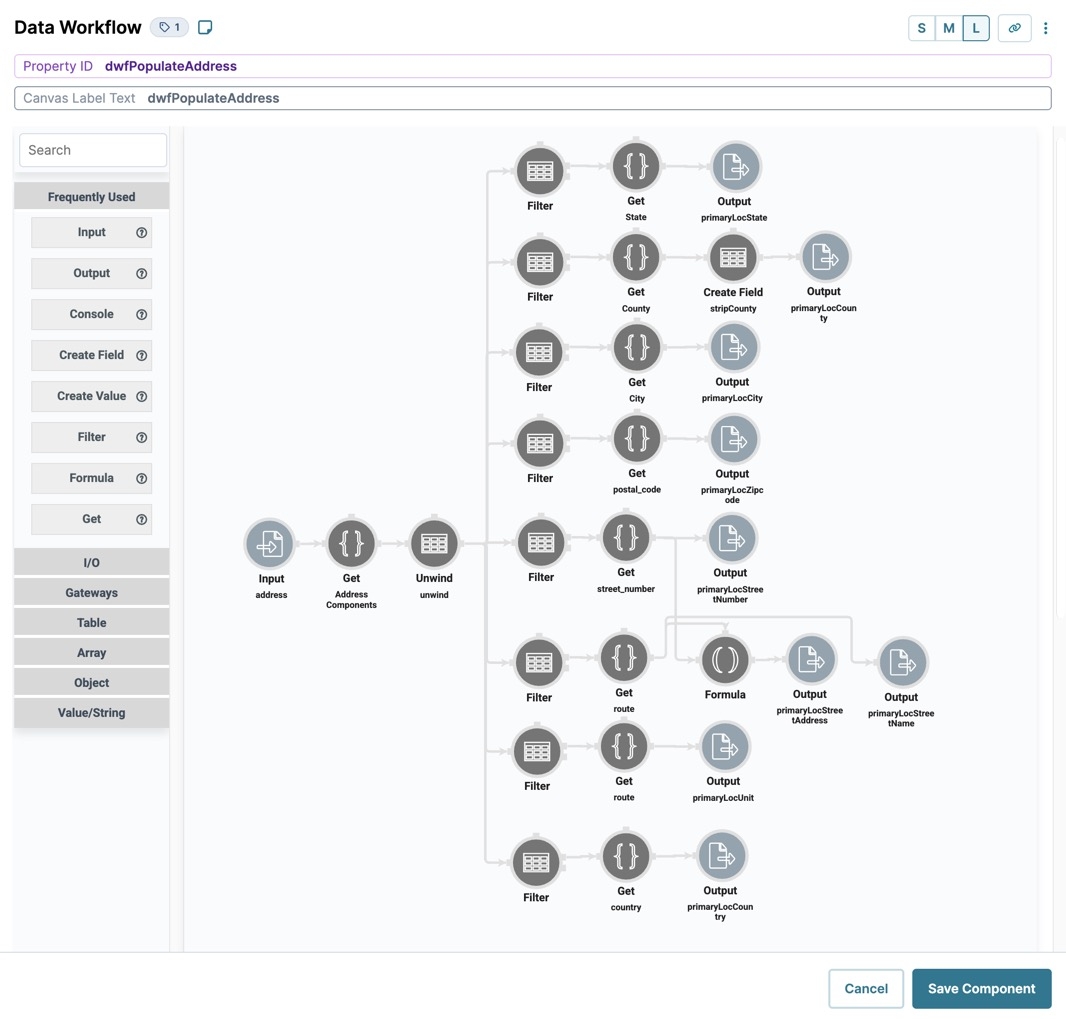
The example below displays the Address Parsing snippet's Data Workflow canvas showing an orchestration of operators.
.jpg)
The Input operator brings in the data from an Address Search component. The Unwind operator separates the individual data points, and the remaining operators take each data point and output it to different fields.
Understanding What Operator Ports Do
DWF Operators have one or more ports that either receive, modify, or output data to and from the operator. In some cases, an operator can also have more than one input or output port. Below are the ports you'll see associated with a Filter operator:
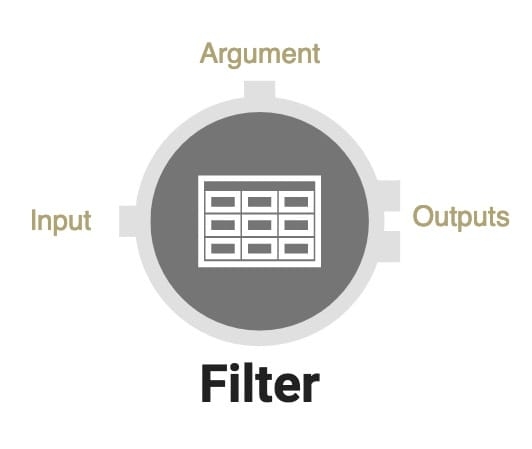
Click on the tabs below to learn more about what each operator port does:
Input Port (Left)
The input port is the entry point into your operator. The previous operator in the Data Workflow connects to the next operator's input port.
Some data operations have two inputs. For example, the Merge operator combines two input data sets. In this case, a data set enters Input 1, and another data set enters Input 2.
Argument Port (Top)
Arguments add a dynamic aspect to data processing. They can create conditions, rules, and more functionality for an operator. When you bring an input into an operator's top port, you're bringing the input in as an argument.
It's important to make a distinction between an argument and an expression. Most operators have an Expression or Key field that controls what the operator does. For example, say you have a data set of savings accounts and checking accounts. You want to filter the two account types into separate outputs using a Filter operator. Without an argument, your expression might be account="savings". From there, the savings accounts filter output to another operator. Anything that isn't a savings account filters out from the rest. The operator performs a single operation. If you want an operator to always have the same function, there's no need for an argument.
Where an argument comes into play is when you want different functions based on dynamic data. Let's use the example of a data set of savings and checking accounts. With an argument, you can make the filter more complex. You could add more filtering operations, like sorting accounts by their size. You could also add logic to your filter, calculating multiple account sizes. Or, you could set up decision based on the accounts your end-user selects.
Unqork references an argument as
_argin an expression.
Output Port (Right)
Outputs are where you send the final result of the operation. You'll connect one output to the next using the right port.
Some data operations have two outputs. For example, the Filter operator, which separates data and outputs into multiple locations. Output 1 would be all the expression results that are true, or what you filtered for. Output 2 would be the expression results that are false, or what you do not what to filter for.
.jpg)
Connecting Operators
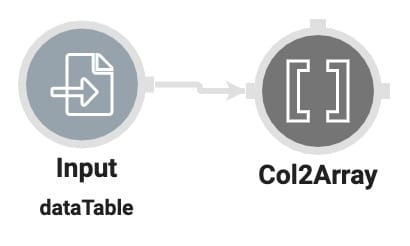
Connect operators to send logic and data between them. Creators connect operators by clicking and holding their mouse on an output port and dragging it to an input or argument port. In the following image, the output port (right) of the Input operator connects to the input port (left) of the Col2Array operator.
Grouping Operators
Grouping operators can help organize a Data Workflow's canvas. Doing so creates a clear process flow and helps you track your operators' functions.
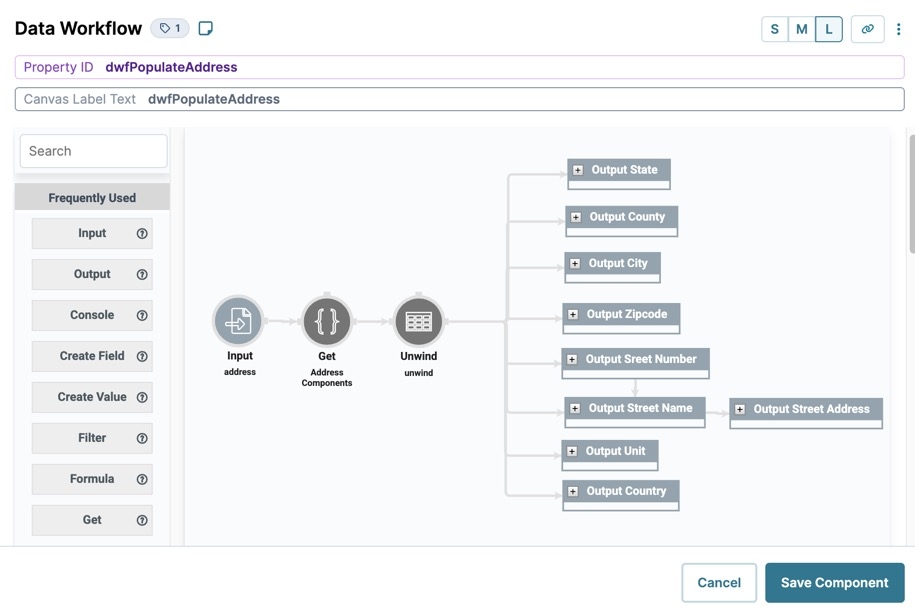
Let's look at the Address Parsing snippet before grouping, and after grouping the operators:
By default, the Address Parsing snippet's Data Workflow canvas looks like the following:
Applying groups to the Address Parsing snippet's Data Workflow canvas looks like the following:
To group Data Workflow operators:
Press and hold the Shift key while clicking on the Data Workflow operators you want to group.
Press the Ctrl + G keys (PC) or Cmd + G keys (Mac). The selected operators group together, then collapse into an expandable frame.
You can expand or collapse the frame by clicking the plus (+) or minus (-) sign in the frame's top bar.
In the Info window that displays, enter a Label for your group of operations.
Click Save Component.
Data Workflow Operators
The Data Workflow component's operators are organized into six categories, based on the actions they perform. Click the following links to learn more about the various Data Workflow categories:
I/O Operators
I/O operators let you input data, create tables and values, and output data to components. They include the Input, Create Table, Output, and Console operators.
Gateways Operators
These operators let you introduce decision logic, control Data Workflow pathways, and merge and split branches. They include the Branch Split and Branch Merge, Decision, and Input Switch operators.
Table Operators
Table operators let you append and merge tables, create a nested table, and output data as a string or an object. They include the Append, Create Field, Merge, Nest By, and Table2Object operators.
Array Operators
These operators let you retrieve data from a data set, add values to a data structure, and join an array of values. They include the Array2Col, Get, Join, and Set operators.
Object Operators
These operators let you remove null values, create a table into an object, and merge two objects into one. They include the Clean Object, Diff, Extend, and Has operators.
Value/String Operators
These operators let you convert Excel files into JSON, convert a JSON string to a JSON object, and find matching values in a table. They include the Convert Value, Formula, NLP, and Split String operators.
Frequently Used
There is also a frequently-used Data Workflow operator category. Below is a list of these Data Workflow operators with a description of how they work.
Operator | Description |
|---|---|
Lets you retrieve data from another component and bring it into your Data Workflow. Use the Component drop-down to select an existing component in your module. Set Required to | |
An Output operator marks the end of a Data Workflow path. Use the Component setting to select a component in your module to output the data. The Action setting applies to the component selected in the Component field. This operator is commonly used for outputting data by setting the Action field to
| |
Watches the progress of data passing through your Data Workflow operators. This operator is useful for monitoring and troubleshooting individual steps in the DevTools Console.
| |
Creates or updates key/value pairs (fields) in a table. Use the structure key=value or key="value" for strings. The operator also supports conditional expressions and referencing other values. Use the structure
| |
Lets you create a value and pass it into the Data Workflow. This operator can create a number, string, or Boolean value. You can either set the value directly in the Value/Expression field or use | |
Filters table-based data using the criteria specified in the Expression field. The operator separates rows that meet the criteria from rows that do not. Matching rows pass through the upper output port while non-matching rows pass through the lower output port. For example, to filter for rows containing the key/value pair "member":"yes", use the Expression member="yes".
| |
Performs calculations on your data based on the formula defined in the Formula/Expression field. You can use an alias of | |
Retrieves data from your data set based on the value entered in the Path field. You can use the operator to retrieve individual values or entire rows of an array. For example, a Path of
|
Best Practices
For operators that require fields, like the Formula operator, it is best practice to avoid using symbols and numerical values in the fields. For example, instead of using
Test1Key="value",useTestOneKey="value".Data Workflows timeout after five minutes in all environments. Build Data Workflows to complete operations in five minutes to prevent timeouts.
If you don't plan to use disabled components in your application, remove them to ensure optimal performance. Remember to check all active components that connect to disabled components. Ensure active components still function properly after you remove the disabled ones.
Add labels to all Data Workflow operators to describe their function. These labels make it easier to know the purpose of an operator without having to open the Info window.
Select the Do Not Sanitize setting in all your operators to improve application performance.
Organize Data Workflow components based on their function in your application.
Use the component's Notes tab to comment on complex data processes. Add notes to explain what components are being triggered, trigger types, and the importance of each component.