Unqork’s Application Versioning lets Creators save, label, and manage different iterations of their application. In other words, Unqork application versions give you structured control over application changes and updates, making it easier to manage releases, maintain compliance, and scale governance across multiple teams.
How Application Versions Work?
When Creators create a new application version, Unqork captures the full application state (modules, workflows, and configurations). You can manage these application versions using the Promotions and Versions page. This page includes the following tabs:
Promotion History: Use this tab to promote application versions to another environment level and view your promotion history.
Set Default Version: Use this tab to adjust the default application version. The default version of an application is the version that displays if no context is provided in the application URL. This is also the version of the application that will be used if another application sets the default as a dependency. This tab is useful when an issue occurs in your current default application version, and you need to return to the previous one.
Best Practices: Naming Application Versions
It’s important to understand the concept of major, minor, and patch versions before exploring the best practices for naming application versions:
Major: A major version includes architectural changes, new significant functionality, or a substantial update to an application.
Minor: A minor version includes small updates that help to improve application performance, all while maintaining backward compatibility.
Patch: A patch version includes bug fixes or other small fixes to improve the performance of an existing version.
Below are some best practices for numbering application versions in Unqork:
We recommend using the automated numbering populated by selecting a major, minor, or patch update type. This uses the Semantic Versioning Principle of
Major.Minor.Patchformat in the Version Number field. For example, setting a Version Number for a Major release to1.0.0, as shown below.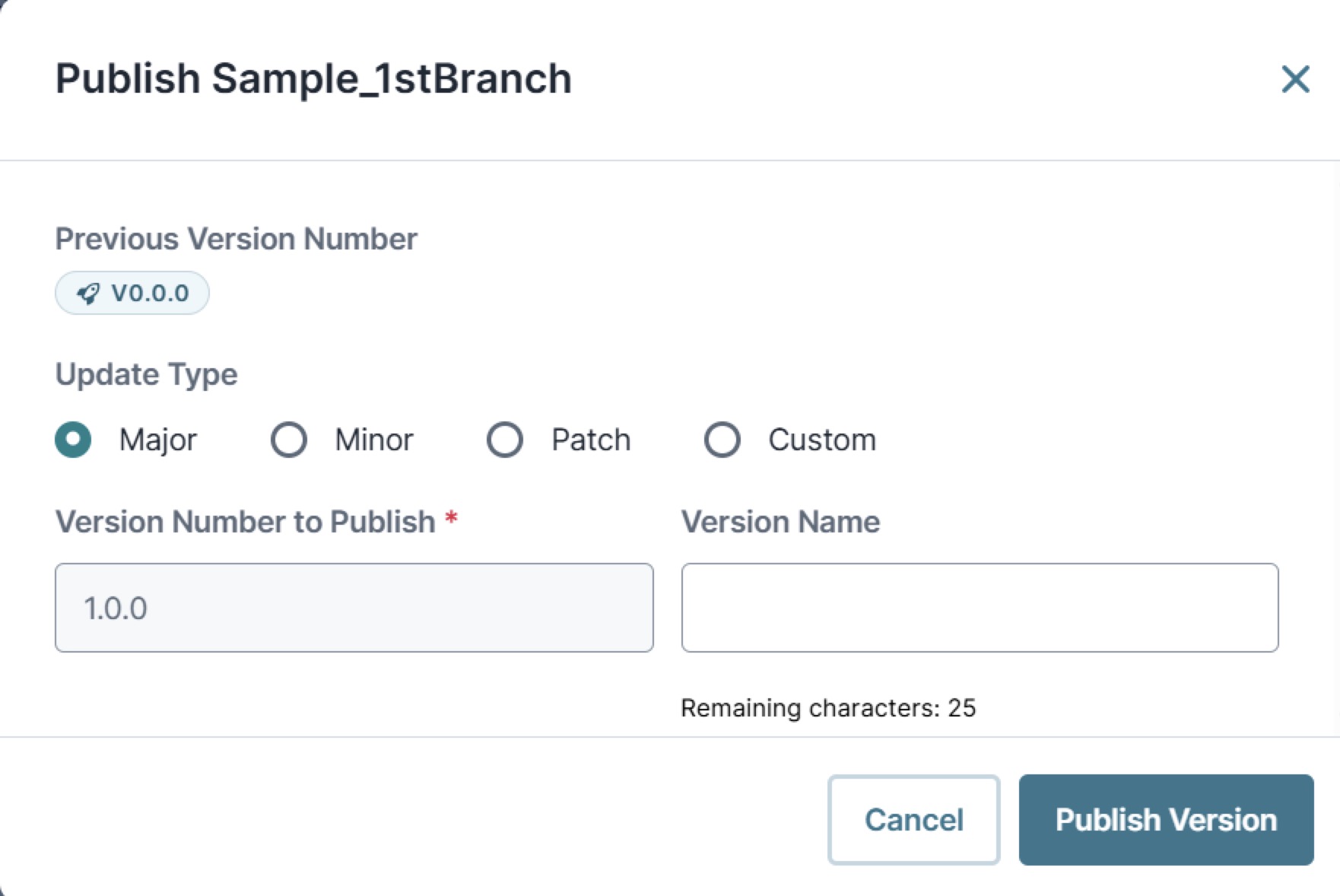
Keep version names consistent according to conventions set up by your team.
Application Versioning Boundaries
When Creators create an application version in Unqork, it includes the following application elements:
Application Modules (logic, schema, workflows, rules, validations)
Application Pages/Layouts (UI components)
Application Settings (navigation, metadata, app-level configurations)
Workflow Configurations
Certain elements are not included at the time of application version creation. These elements sit outside versioning and are not tied to a specific application version:
Data Collections: The data stored in the environment is not captured with application versions; only the structure and logic are captured.
Managed Assets: Files in Managed Assets, like PDFs, Images, or CSS, are not captured with application versions.
Environment Level Configurations: Application integrations, RBAC policies, and SSO settings are not captured with application versions.
Role Permissions: Access permissions within the application applied to modules or components are included.
External Services/APIs: In application versioning, only references are stored; external services and APIs are not part of the version.
Versioning boundaries ensure a clear separation of state between Staging, UAT, and Production. A version created in Staging does not automatically display in UAT or Production; it needs to be promoted.